Generate Encryption Keys For The Card Data
- Types Of Data Encryption
- Generate Encryption Keys For The Card Data Online
- Generate Encryption Keys For The Card Data Center
 -->
-->- The Case for Strong Encryption Keys 27th April 2017 The strength of any cryptographic system lies in its keys – the random stream of bits used by the cryptographic algorithm to transform plain text into cypher text and back again.
- The IPEK and KSN are then used to derive the key for that specific transaction/swipe. Once the developer has this key they can easily decrypt the card data. Generating the IPEK. In order to generate the Initial Pin Encryption Key (IPEK) we need the Base Derivation Key (BDK) and the Key Serial Number (KSN). The IPEK is derived using TripleDES encryption.
How are biometric characteristics used to generate encryption keys. I don't think any biometrical characteristics are used to generate any encryption keys. One of the most valuable properties of encryption key is high entropy (randomness, uniqueness) which imho cannot be directly achieved by biometric readings. Finally, gpg2 generates random data to make your key as unique as possible. Move your mouse, type random keys, or perform other tasks on the system during this step to speed up the process. Move your mouse, type random keys, or perform other tasks on the system during this step to speed up the process.
Deleting and recreating encryption keys are activities that fall outside of routine encryption key maintenance. You perform these tasks in response to a specific threat to your report server, or as a last resort when you can no longer access a report server database.
Recreate the symmetric key when you believe the existing symmetric key is compromised. You can also recreate the key on a regular basis as a security best practice.
Delete existing encryption keys and unusable encrypted content when you cannot restore the symmetric key.
Recreating Encryption Keys
If you have evidence that the symmetric key is known to unauthorized users, or if your report server has been under attack and you want to reset the symmetric key as a precaution, you can recreate the symmetric key. When you recreate the symmetric key, all encrypted values will be re-encrypted using the new value. If you are running multiple report servers in a scale-out deployment, all copies of the symmetric key will be updated to the new value. The report server uses the public keys available to it to update the symmetric key for each server in the deployment.
You can only recreate the symmetric key when the report server is in a working state. Recreating the encryption keys and re-encrypting content disrupts server operations. You must take the server offline while re-encryption is underway. There should be no requests made to the report server during re-encryption.
You can use the Reporting Services Configuration tool or the rskeymgmt utility to reset the symmetric key and encrypted data. For more information about how the symmetric key is created, see Initialize a Report Server (SSRS Configuration Manager).
How to recreate encryption keys (Reporting Services Configuration Tool)
Disable the Report Server Web service and HTTP access by modifying the IsWebServiceEnabled property in the rsreportserver.config file. This step temporarily stops authentication requests from being sent to the report server without completely shutting down the server. You must have minimal service so that you can recreate the keys.
If you are recreating encryption keys for a report server scale-out deployment, disable this property on all instances in the deployment.
Open Windows Explorer and navigate to drive:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL Serverreport_server_instanceReporting Services. Replace drive with your drive letter and report_server_instance with the folder name that corresponds to the report server instance for which you want to disable the Web service and HTTP access. For example, C:Program FilesMicrosoft SQL ServerMSRS10_50.MSSQLSERVERReporting Services.
Open the rsreportserver.config file.
For the IsWebServiceEnabled property, specify False, and then save your changes.
Start the Reporting Services Configuration tool, and then connect to the report server instance you want to configure.
On the Encryption Keys page, click Change. Click OK.
Restart the Report Server Windows service. If you are recreating encryption keys for a scale-out deployment, restart the service on all instances.
Re-enable the Web service and HTTP access by modifying the IsWebServiceEnabled property in the rsreportserver.config file. Do this for all instances if you are working with a scale out deployment.
Types Of Data Encryption
How to recreate encryption keys (rskeymgmt)
Disable the Report Server Web service and HTTP access. Use the instructions in the previous procedure to stop Web service operations.
Run rskeymgmt.exe locally on the computer that hosts the report server. Use the -s argument to reset the symmetric key. No other arguments are required:
Restart the Reporting Services Windows service.
Deleting Unusable Encrypted Content
If for some reason you cannot restore the encryption key, the report server will never be able to decrypt and use any data that is encrypted with that key. To return the report server to a working state, you must delete the encrypted values that are currently stored in the report server database and then manually re-specify the values you need.
Deleting the encryption keys removes all symmetric key information from the report server database and deletes any encrypted content. All unencrypted data is left intact; only encrypted content is removed. When you delete the encryption keys, the report server re-initializes itself automatically by adding a new symmetric key. The following occurs when you delete encrypted content:
Connection strings in shared data sources are deleted. Users who run reports get the error 'The ConnectionString property has not been initialized.'
Stored credentials are deleted. Reports and shared data sources are reconfigured to use prompted credentials.
Reports that are based on models (and require shared data sources configured with stored or no credentials) will not run.
Subscriptions are deactivated.
Once you delete encrypted content, you cannot recover it. You must re-specify connection strings and stored credentials, and you must activate subscriptions.
You can use the Reporting Services Configuration tool or the rskeymgmt utility to remove the values.
How to delete encryption keys (Reporting Services Configuration Tool)
Start the Reporting Services Configuration tool, and then connect to the report server instance you want to configure.
Click Encryption Keys, and then click Delete. Click OK.
/mac-generate-new-ssh-key.html. Restart the Report Server Windows service. For a scale-out deployment, do this on all report server instances.
How to delete encryption keys (rskeymmgt)
Run rskeymgmt.exe locally on the computer that hosts the report server. You must use the -d apply argument. The following example illustrates the argument you must specify:
Restart the Report Server Windows service. For a scale-out deployment, do this on all report server instances.
How to re-specify encrypted values
For each shared data source, you must retype the connection string.
For each report and shared data source that uses stored credentials, you must retype the user name and password, and then save. For more information, see Specify Credential and Connection Information for Report Data Sources.
For each data-driven subscription, open each subscription and retype the credentials to the subscription database.
For subscriptions that use encrypted data (this includes the File Share delivery extension and any third-party delivery extension that uses encryption), open each subscription and retype credentials. Subscriptions that use Report Server e-mail delivery do not use encrypted data and are unaffected by the key change.
See Also
Configure and Manage Encryption Keys (SSRS Configuration Manager)
Store Encrypted Report Server Data (SSRS Configuration Manager)
Creating and managing keys is an important part of the cryptographic process. Symmetric algorithms require the creation of a key and an initialization vector (IV). The key must be kept secret from anyone who should not decrypt your data. The IV does not have to be secret, but should be changed for each session. Asymmetric algorithms require the creation of a public key and a private key. The public key can be made public to anyone, while the private key must known only by the party who will decrypt the data encrypted with the public key. This section describes how to generate and manage keys for both symmetric and asymmetric algorithms.
Symmetric Keys
Generate Encryption Keys For The Card Data Online
The symmetric encryption classes supplied by the .NET Framework require a key and a new initialization vector (IV) to encrypt and decrypt data. Whenever you create a new instance of one of the managed symmetric cryptographic classes using the parameterless constructor, a new key and IV are automatically created. Anyone that you allow to decrypt your data must possess the same key and IV and use the same algorithm. Generally, a new key and IV should be created for every session, and neither the key nor IV should be stored for use in a later session.
To communicate a symmetric key and IV to a remote party, you would usually encrypt the symmetric key by using asymmetric encryption. Sending the key across an insecure network without encrypting it is unsafe, because anyone who intercepts the key and IV can then decrypt your data. For more information about exchanging data by using encryption, see Creating a Cryptographic Scheme.
The following example shows the creation of a new instance of the TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider class that implements the TripleDES algorithm.
When the previous code is executed, a new key and IV are generated and placed in the Key and IV properties, respectively.
Generate Encryption Keys For The Card Data Center
Sometimes you might need to generate multiple keys. In this situation, you can create a new instance of a class that implements a symmetric algorithm and then create a new key and IV by calling the GenerateKey and GenerateIV methods. The following code example illustrates how to create new keys and IVs after a new instance of the symmetric cryptographic class has been made.
When the previous code is executed, a key and IV are generated when the new instance of TripleDESCryptoServiceProvider is made. Another key and IV are created when the GenerateKey and GenerateIV methods are called.
Asymmetric Keys
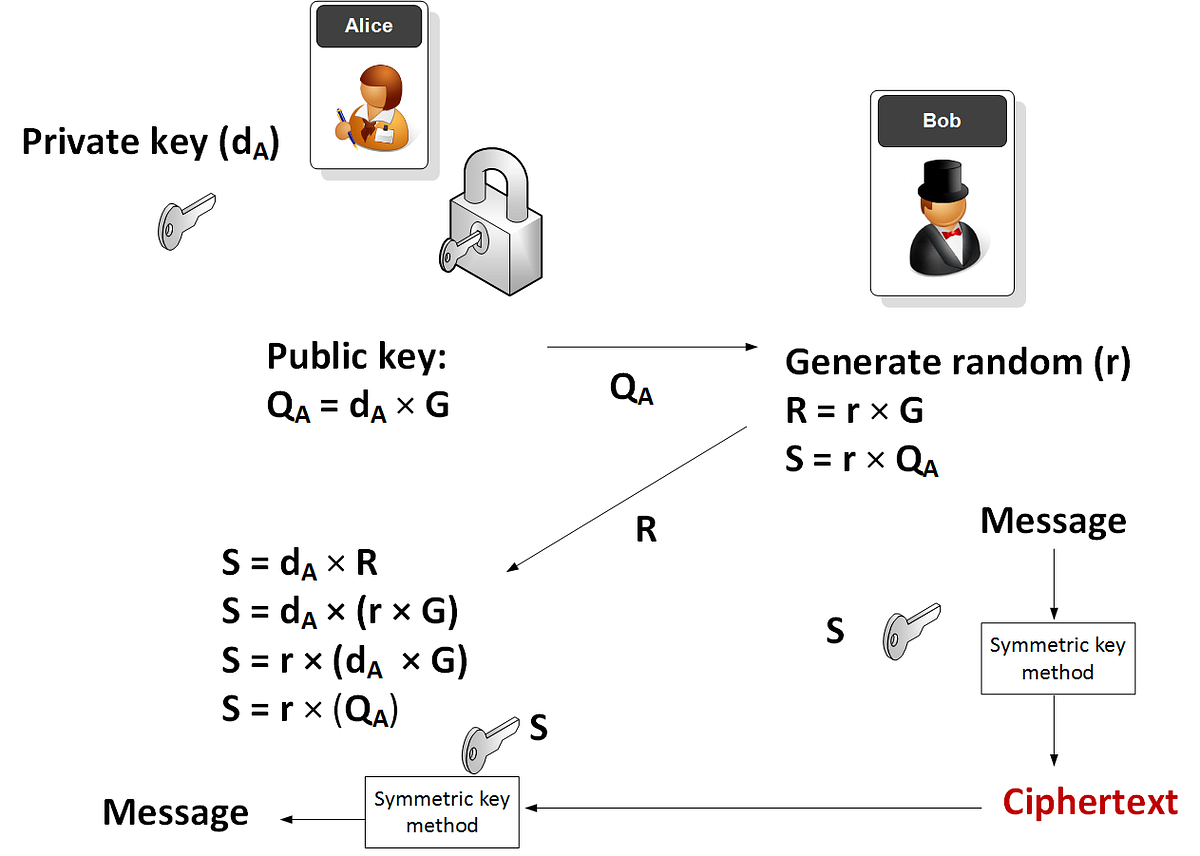
The .NET Framework provides the RSACryptoServiceProvider and DSACryptoServiceProvider classes for asymmetric encryption. These classes create a public/private key pair when you use the parameterless constructor to create a new instance. Asymmetric keys can be either stored for use in multiple sessions or generated for one session only. While the public key can be made generally available, the private key should be closely guarded.
A public/private key pair is generated whenever a new instance of an asymmetric algorithm class is created. After a new instance of the class is created, the key information can be extracted using one of two methods:
The ToXmlString method, which returns an XML representation of the key information.
The ExportParameters method, which returns an RSAParameters structure that holds the key information.
Both methods accept a Boolean value that indicates whether to return only the public key information or to return both the public-key and the private-key information. An RSACryptoServiceProvider class can be initialized to the value of an RSAParameters structure by using the ImportParameters method.
Asymmetric private keys should never be stored verbatim or in plain text on the local computer. If you need to store a private key, you should use a key container. For more on how to store a private key in a key container, see How to: Store Asymmetric Keys in a Key Container.
The following code example creates a new instance of the RSACryptoServiceProvider class, creating a public/private key pair, and saves the public key information to an RSAParameters structure.