Group Secret Key Generation Algorithms
Nov 04, 2014 Meet Eddie Woo, the maths teacher you wish you’d had in high school Australian Story - Duration: 28:09. ABC News In-depth Recommended for you. Distributed key generation: For some protocols, no party should be in the sole possession of the secret key. Rather, during distributed key generation, every party obtains a share of the key. A threshold of the participating parties need to cooperate to achieve a cryptographic task, such as decrypting a message.
In particular, this group key generation process is studied for three types of communication networks: 1) the three-node network, 2) the multi-node ring network and 3) the multi-node mesh network. Three group key generation algorithms are developed. Distributed key generation prevents single parties from having access to a private key. The involvement of many parties requires Distributed key generation to ensure secrecy in the presence of malicious contributions to the key calculation. Distributed Key Generation is commonly used to decrypt shared ciphertexts or create group digital signatures. The key for the AES encryption should be exchanged with the Diffie-Hellman (DH) algorithm. Now, I've read about DH and got a lot of question marks over my head. These are my questions: Typically with AES-128, you need a password and a key which will be generated from the password. Three group key generation algorithms are developed for these communication networks, respectively. The analysis shows that the first two algorithms yield optimal group key rates, whereas the third algorithm achieves the optimal multiplexing gain.
Key generation is the process of generating keys for cryptography. The key is used to encrypt and decrypt data whatever the data is being encrypted or decrypted.
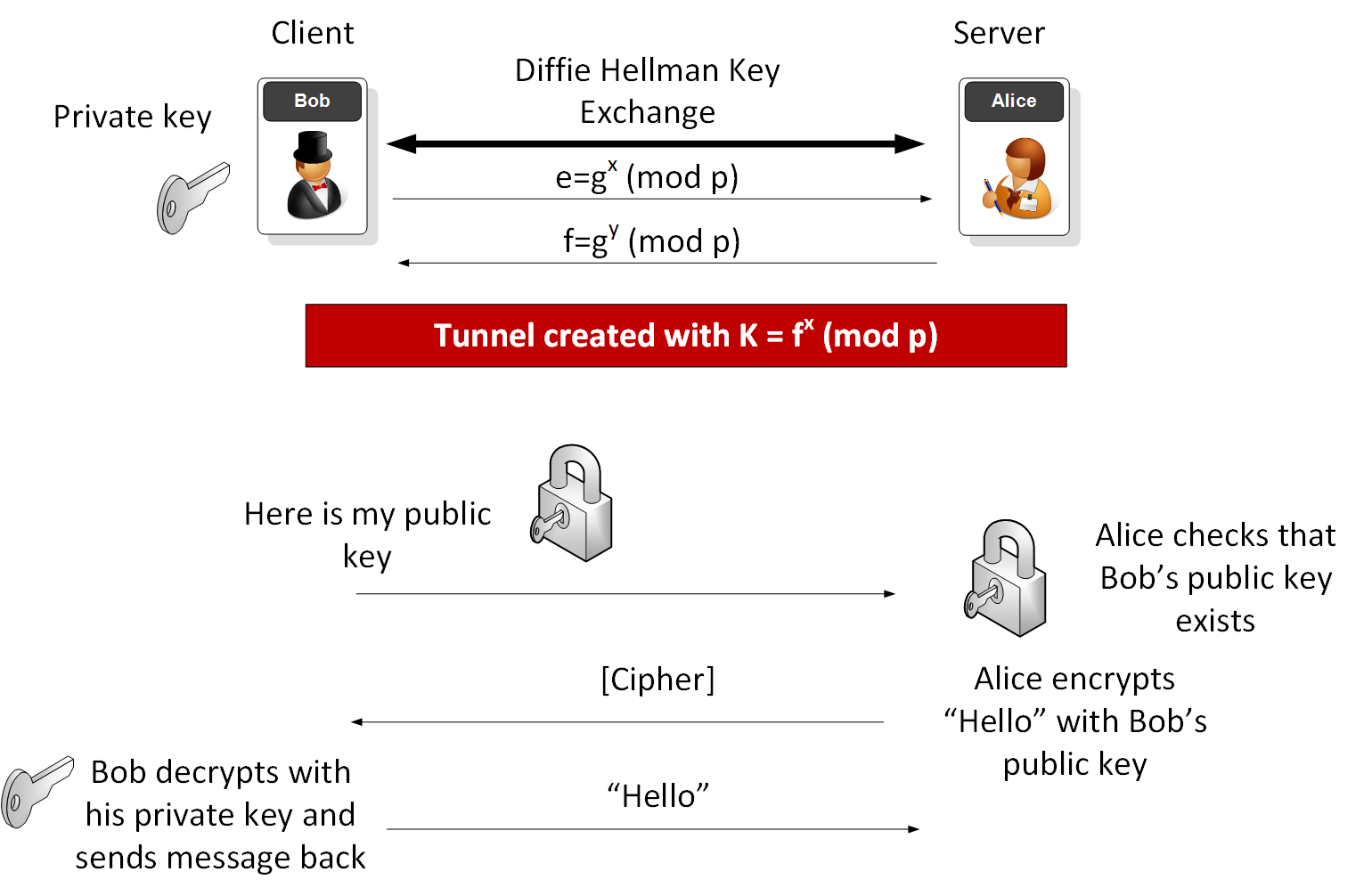
Modern cryptographic systems include symmetric-key algorithms (such as DES and AES) and public-key algorithms (such as RSA). Symmetric-key algorithms use a single shared key; keeping data secret requires keeping this key secret. Public-key algorithms use a public key and a private key. The public key is made available to anyone (often by means of a digital certificate). A sender will encrypt data with the public key; only the holder of the private key can decrypt this data.
Since public-key algorithms tend to be much slower than symmetric-key algorithms, modern systems such as TLS and its predecessor SSL as well as the SSH use a combination of the two in which:
- One party receives the other's public key, and encrypts a small piece of data (either a symmetric key or some data that will be used to generate it).
- The remainder of the conversation (the remaining party) uses a (typically faster) symmetric-key algorithm for encryption.
The simplest method to read encrypted data is a brute force attack–simply attempting every number, up to the maximum length of the key. Therefore, it is important to use a sufficiently long key length; longer keys take exponentially longer time to attack, making a brute force attack invisible and impractical.
Currently, commonly used key lengths are:
- 128-bits for symmetric key algorithms.
- 1024-bits for public-key algorithms.
Key generation algorithms[changechange source]
In computer cryptography keys are integers. In some cases keys are randomly generated using a random number generator (RNG) or pseudorandom number generator (PRNG), the latter being a computeralgorithm that produces data which appears random under analysis. Some types the PRNGs algorithms utilize system entropy to generate a seed data, such seeds produce better results, since this makes the initial conditions of the PRNG much more difficult for an attacker to guess.
In other situations, the key is created using a passphrase and a key generation algorithmKey generator for sims 4 get to work. , using a cryptographic hash function such as SHA-1.
Related pages[changechange source]
- Distributed key generation: For some protocols no party should be in the sole possession of the secret key. Rather, during distributed key generation every party obtains a share of the key. A threshold of the participating parties need to work together in order to achieve a cryptographic task, such as decrypting a message.
References[changechange source]
Key factories are used to convert keys (opaque cryptographic keys of type Key) into key specifications (transparent representations of the underlying key material), and vice versa. Secret key factories operate only on secret (symmetric) keys. Camtasia studio 9 serial key generator.
Key factories are bi-directional, i.e., they allow to build an opaque key object from a given key specification (key material), or to retrieve the underlying key material of a key object in a suitable format.
Application developers should refer to their provider's documentation to find out which key specifications are supported by the generateSecret and getKeySpec methods. For example, the DES secret-key factory supplied by the 'SunJCE' provider supports DESKeySpec as a transparent representation of DES keys, and that provider's secret-key factory for Triple DES keys supports DESedeKeySpec as a transparent representation of Triple DES keys.
Secret Key Skin Care
Every implementation of the Java platform is required to support the following standard SecretKeyFactory algorithms:
National Secret Algorithm
DESDESede